2025 Guide: How to Use a 60 Hz to 50 Hz Frequency Converter Effectively
In today's global economy, machinery often faces the challenge of varying voltage and frequency. A key player in addressing this is the "60 Hz to 50 Hz frequency converter." Renowned expert Dr. Emily Chen, a leader in electrical engineering, states, "Using the right converter is essential for equipment longevity."
Effectively managing the transition from 60 Hz to 50 Hz can enhance performance. Many manufacturers struggle with compatibility issues. Converters not only ensure proper functioning but also prevent costly damages. For example, running a 60 Hz device on a 50 Hz line may lead to overheating or inefficiency. The right frequency converter mitigates such risks, ensuring smooth operations across different regions.
However, users often overlook installation details. Proper configuration is vital and can be tricky. A misunderstanding in settings can result in poor performance. Reflecting on these aspects is crucial for long-term success. Investing time in learning about frequency converters will yield significant benefits in the end.

Understanding the Basics of Frequency Conversion: 60 Hz vs. 50 Hz

Understanding the differences between 60 Hz and 50 Hz is crucial for many industries. The majority of the Americas use 60 Hz, while Europe and Asia predominantly stick to 50 Hz. According to a report by the International Electrotechnical Commission, approximately 80% of the world’s power systems operate at these frequencies. This difference affects electrical devices and their efficiency.
When converting frequencies, one must consider the application. Some equipment does not perform well when switched from 60 Hz to 50 Hz. Motors, for instance, may lose efficiency, leading to overheating. A study published by the IEEE highlights that a 60 Hz motor running at 50 Hz can see a drop in performance by 5% to 15%.
Rethinking the use of frequency converters is essential. They can ensure devices run smoothly across regions that use different frequencies. However, improper usage remains a common issue. Many facilities do not account for load requirements or compatibility issues. In fact, around 30% of converters fail to meet the needs of the devices they serve. This inefficiency can lead to unnecessary downtime and costs. Understanding the nuances of frequency conversion is vital for successful operation.
Importance of Selecting the Right Frequency Converter for Your Equipment
Choosing the right frequency converter for your equipment is crucial. A 60 Hz to 50 Hz frequency converter can make a significant difference. The right choice ensures that your machinery operates at peak efficiency. Mistakes in selection can lead to equipment damage. Overheating or underperformance may occur.
Consider your equipment's specifications carefully. Compatibility is vital. Some devices are sensitive to frequency changes. They may fail if the converter does not match their needs. High-quality converters can handle load variations well. They help maintain device longevity. However, cheap converters often compromise performance and safety.
Be mindful of the installation process too. It's easy to overlook details during setup. Poor connections can lead to power loss. Regular maintenance is essential for optimal functioning. Track the converter's performance over time. If discrepancies arise, re-evaluate your choice. Choosing wisely means considering both immediate needs and future implications.
Step-by-Step Installation Process for a 60 Hz to 50 Hz Converter
Installing a 60 Hz to 50 Hz frequency converter can be challenging. It's vital to follow a straightforward process. Start by selecting a suitable location for the converter. Ensure it's dry and well-ventilated. This will help in maintaining performance.
Next, gather all necessary tools. You will need a screwdriver, pliers, and wire cutters. Familiarize yourself with the wiring diagram that comes with the unit. This step can save time and prevent mistakes.
Then, connect the input wires to the converter. Make sure each wire is secure. Follow the color codes provided. A loose connection can lead to failure. After this, attach the output wires. Double-check all connections before powering on. It’s okay to pause and think if something doesn’t seem right. Install properly to avoid future frustration.
Frequency Converter Efficiency Over Time
This chart illustrates the efficiency of 60 Hz to 50 Hz frequency converters over a span of seven months. The efficiency is shown as a percentage, demonstrating an overall upward trend as the technology improves.
Key Performance Metrics: Efficiency and Power Loss in Frequency Conversion
Frequency converters play a crucial role in optimizing energy usage. When converting from 60 Hz to 50 Hz, efficiency impacts overall performance. A notable industry report indicates that efficiency rates can vary between 90% and 98%. This difference results in significant power loss. Even a fraction of a percentage drop can equate to thousands of lost watts annually.
Power loss during frequency conversion is an essential metric. Research shows that converters can generate heat, leading to inefficiencies. Some models suffer losses exceeding 10% of their input power. This level of inefficiency can greatly increase operational costs. Understanding how to mitigate these losses is vital for organizations aiming for energy efficiency.
Proper maintenance and routine checks can enhance conversion performance. Regular assessments can identify overheating or electrical imbalances. These factors contribute to reduced efficiency. Consider the environmental impact as well. Ultimately, informed decisions on frequency converter usage will help streamline operations and minimize power wastage.
Troubleshooting Common Issues with 60 Hz to 50 Hz Frequency Converters
When using a frequency converter from 60 Hz to 50 Hz, some issues may arise. Users often encounter compatibility problems with their equipment. For instance, motors may overheat or run inefficiently. Such problems can stem from improper settings or load mismatches.
Another common issue involves noise and vibration. Equipment may produce unexpected sounds during operation. This usually indicates an imbalance or mechanical resistance. Regular inspections are crucial. Ensure all connections are secure and that the converter is properly calibrated.
Finally, users might face power fluctuation problems. Voltage drops can influence the performance of sensitive devices. Monitoring voltage levels during operation is essential. If fluctuations persist, consider adjusting the converter or consulting a technician. Frequent troubleshooting can lead to smoother operation and improved efficiency.
Related Posts
-

Understanding the Transition: How a 60 Hz to 50 Hz Frequency Converter Can Enhance Energy Efficiency in Industrial Applications
-

Unlock Equipment Efficiency: How a 60Hz to 50Hz Frequency Converter Enhances Power Usage by 30%
-

How to Choose the Best 60hz to 50hz Frequency Converter for Your Needs
-

How to Convert 60Hz to 50Hz Easily at Home without Any Complications
-

10 Essential Tips for Choosing the Right AC to AC Inverter for Your Needs
-
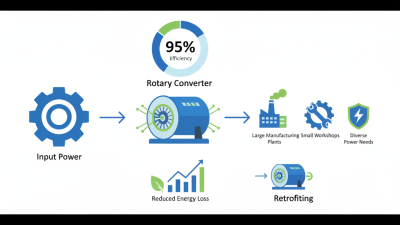
Why You Should Choose a Rotary Converter for Your Power Needs