What Is a 3 Phase Frequency Converter and How Does It Work
A 3 phase frequency converter is an essential device in modern industrial applications, enabling the conversion of electrical power from one frequency to another. According to a market analysis report by Global Industry Analysts, the global demand for frequency converters is expected to reach $11 billion by 2026, driven by their increasing use in various sectors, including renewable energy, manufacturing, and automation. This technology plays a vital role in enhancing energy efficiency and providing precise control over motor speeds, making it indispensable for industrial operations that rely on three-phase power systems.
As noted by Dr. Emily Turner, a leading expert in energy systems, “The integration of a 3 phase frequency converter not only optimizes operational performance but also reduces energy consumption significantly.” This statement underscores the growing relevance of frequency converters in addressing the challenges of energy management and sustainability. By enabling smoother power adjustments and improving the reliability of electric systems, 3 phase frequency converters are paving the way for more innovative and efficient industrial processes. With the ongoing advancements in technology and increasing awareness of energy conservation, the role of frequency converters in the industrial landscape is more critical than ever.

What is a Three-Phase Frequency Converter?
A three-phase frequency converter is an essential device used to control the frequency and voltage of electrical power supplied to equipment. It plays a critical role in various industrial applications where there is a need for precise control over motor speeds and torque. By converting the input power from one frequency to another, this converter ensures that machinery operates efficiently and reliably, regardless of the power supply’s variation in frequency.
The working principle of a three-phase frequency converter involves several stages. Initially, it employs a rectifier to convert incoming alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC). Following this, the DC power is processed through an inverter that transforms it back into three-phase AC at the desired frequency. This allows the output to be tailored specifically to match the requirements of the connected equipment. Key benefits of using a three-phase frequency converter include improved energy efficiency, reduced wear and tear on motors, and enhanced control over operational parameters, which can lead to significant cost savings in the long run.
What Is a 3 Phase Frequency Converter and How Does It Work?
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Definition | A device that converts the frequency of electrical power for three-phase systems. |
| Operation | It alters the frequency of input power to match the requirements of the connected load. |
| Applications | Used in industrial motors, HVAC systems, and renewable energy sources. |
| Benefits | Enhances energy efficiency, improves equipment lifespan, and supports variable speed control. |
| Types | Includes static converters, rotary converters, and digital frequency converters. |
| Challenges | Can be complex to install and require maintenance; might introduce harmonic distortion. |
Key Applications of Three-Phase Frequency Converters in Industry
Three-phase frequency converters play a crucial role in various industrial applications by facilitating efficient power conversion and motor control. These devices allow for the adjustment of frequency and voltage supplied to three-phase motors, enabling them to operate at optimal performance levels across varying loads and speeds. In industries where machinery requires diverse operating conditions, three-phase frequency converters become indispensable for enhancing energy efficiency and extending equipment lifespan.
Key applications of three-phase frequency converters are found in manufacturing, HVAC systems, and renewable energy sectors. In manufacturing environments, these converters enable precise control of conveyor belts and robotic arms, ensuring accurate and synchronized operations. HVAC systems utilize frequency converters to optimize fan and pump speeds, resulting in reduced energy consumption and improved climate control. Additionally, in the renewable energy sector, three-phase frequency converters are employed in wind and solar power systems to convert the generated electricity into a stable output that can be fed into the grid, further supporting sustainable energy initiatives. Their ability to enhance performance and efficiency makes them a vital component in modern industrial applications.
Key Applications of Three-Phase Frequency Converters in Industry
Three-phase frequency converters are essential in various industrial applications. The following chart illustrates the relative distribution of their applications across different sectors.
Understanding the Operating Principles of Frequency Conversion
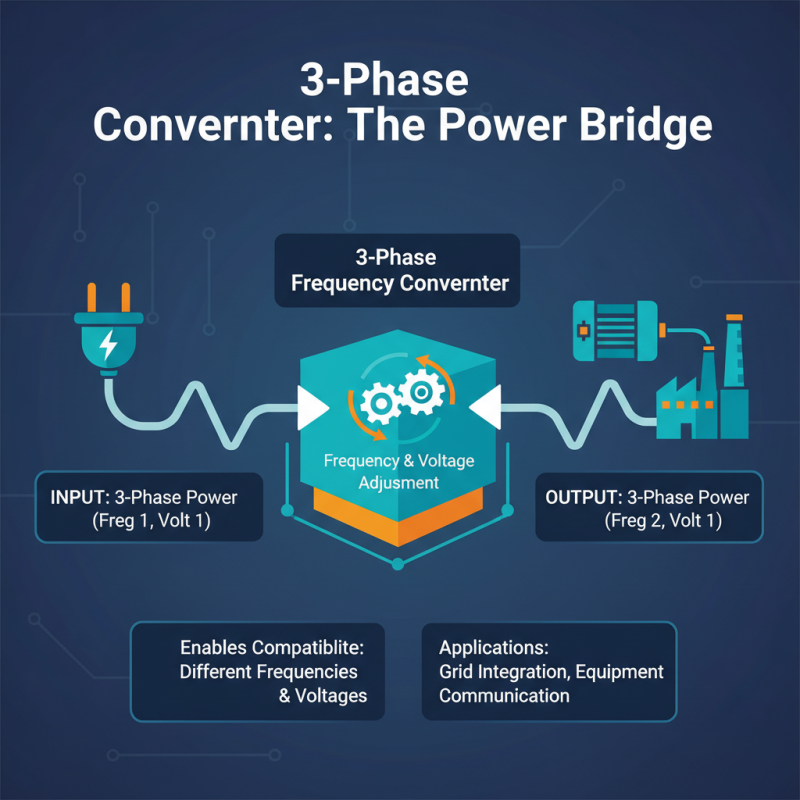
A 3 Phase Frequency Converter is a crucial device that enables the conversion of electrical frequency and voltage from one level to another, while maintaining the three-phase power efficiency. The fundamental principle of frequency conversion involves adjusting the frequency of the incoming power supply, allowing electrical equipment designed for different operational frequencies to function correctly. This process is essential for applications where equipment needs to communicate effectively with varying power sources or when integration into a grid with different frequency standards is necessary.
The operation of a frequency converter typically involves two main stages: rectification and inversion. Initially, the converter rectifies the incoming alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC), which allows for the stabilization and regulation of power. Following this stage, the DC power is then inverted back into AC at the desired frequency through the use of sophisticated electronic components. This two-step process ensures that the output maintains the required specifications, enabling seamless operation of motors, drives, and other systems that are dependent on specific frequency levels. By understanding these operating principles, engineers can effectively design and implement frequency converters to meet the diverse needs of industrial and commercial applications.
Technical Specifications and Efficiency Ratings of Frequency Converters
Frequency converters are essential devices that facilitate the conversion of electrical power from one frequency to another, particularly in three-phase systems. When discussing their technical specifications, it is important to consider aspects such as voltage rating, input and output frequency ranges, and power capacity. A well-designed frequency converter typically accommodates various input voltages and provides stable output suitable for different applications. The capability to handle load variations without significant performance degradation is also a critical indicator of a frequency converter's reliability and versatility.
Efficiency ratings play a crucial role in determining the operational cost-effectiveness of frequency converters. Higher efficiency ratings imply lower energy losses during the conversion process, which can lead to substantial savings over time. Typical efficiency ratings for quality frequency converters range between 90% to 98%, depending on the specific design and application. Factors such as the type of control technology employed—whether it's scalar or vector control—also influence efficiency. Therefore, when selecting a frequency converter, it is vital to evaluate both its technical specifications and efficiency ratings to ensure optimal performance in meeting industrial or commercial needs.
Comparative Analysis of Phase Converter Types: Advantages and Limitations
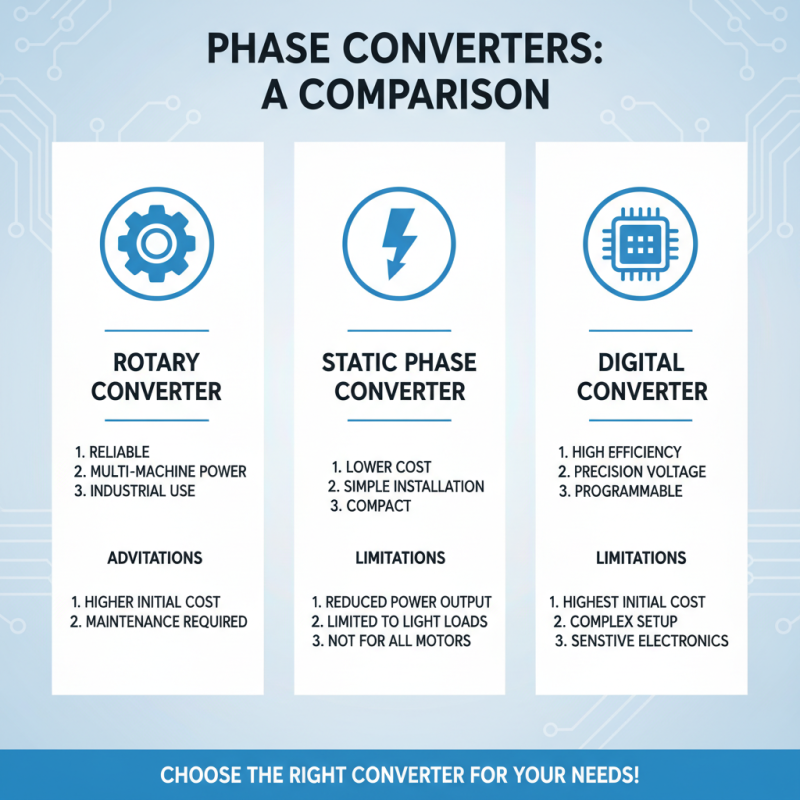
When considering the use of phase converters for various applications, it’s crucial to understand the advantages and limitations of each type. The primary types include rotary phase converters, static phase converters, and digital phase converters. Rotary phase converters are known for their reliability and ability to power multiple machines simultaneously, making them ideal for industrial settings. However, their higher initial cost and maintenance requirements can be a drawback.
On the other hand, static phase converters are typically more affordable and easier to install, making them suitable for small workshops or home use. They are limited, however, as they only provide enough power for one machine at a time and may not support heavy loads. Digital phase converters offer more advanced control and efficiency but can come with a steeper price tag. Understanding these key differences will help you select the right converter based on your specific needs.
Tip: When choosing a phase converter, consider both the power requirements of your equipment and your budget. Consulting with an expert can also provide insights into which converter type will be most effective for your intended applications. Another tip is to assess the scalability of the phase converter to ensure it remains viable as your power needs grow or change.
Related Posts
-

Unlocking Efficiency: How 3 Phase Frequency Converters Revolutionize Industrial Operations
-

The Future of Solid State Frequency Converters Redefining Power Management
-

Understanding Phase Converter 1 to 3 Benefits and Applications for Your Needs
-

How to Choose the Best 60hz to 50hz Frequency Converter for Your Needs
-

Ultimate Guide to 400Hz to 60Hz Converters: Top Picks for 2025
-

Top 5 Three Phase Converters: Enhance Efficiency and Power Quality