How to Choose the Best Single Phase to Three Phase Converter for Your Needs
In the world of electrical engineering and industrial applications, the demand for converting single-phase power to three-phase systems has surged dramatically. According to a report by the International Energy Agency, the global market for power converters is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.5% from 2022 to 2028. This growth is largely attributed to the increasing need for high-efficiency electrical systems in manufacturing and commercial facilities. As industries seek to optimize their power usage, understanding how to choose the best single phase to three phase converter becomes crucial.
Industry expert Dr. Emily Tran, a renowned electrical engineer, emphasizes the importance of proper selection: "Choosing the right single phase to three phase converter can significantly improve the operational efficiency and lifespan of your equipment." Her insights highlight the necessity of evaluating factors such as power requirements, load characteristics, and voltage stability when making a decision. As businesses increasingly rely on three-phase power for their machinery and processes, making an informed choice in converters not only enhances performance but also reduces long-term operational costs. This guide aims to unravel the complexities involved in selecting the optimal single phase to three phase converter tailored to meet specific needs.

Understanding the Basics of Single Phase and Three Phase Power Systems
Understanding the differences between single phase and three phase power systems is essential when selecting the right converter for your needs. Single phase power typically consists of two wires—one live wire and one neutral wire—delivering electricity to homes and smaller appliances. This system is sufficient for light loads, such as residential lighting and small motors, but it may struggle with larger machines requiring more power.
On the other hand, three phase power is composed of three live wires and can deliver power more efficiently and evenly. This system is commonly used in industrial applications and larger equipment due to its ability to provide a constant and balanced power supply. Because three phase systems can handle larger loads with less wiring and reduce power loss, they are often more desirable for high-performance machinery. Understanding these basic differences will guide you in selecting a converter that meets your power demands effectively, ensuring optimal performance for your specific applications.
Power Systems Comparison: Single Phase vs Three Phase
Identifying Your Specific Power Requirements for Equipment
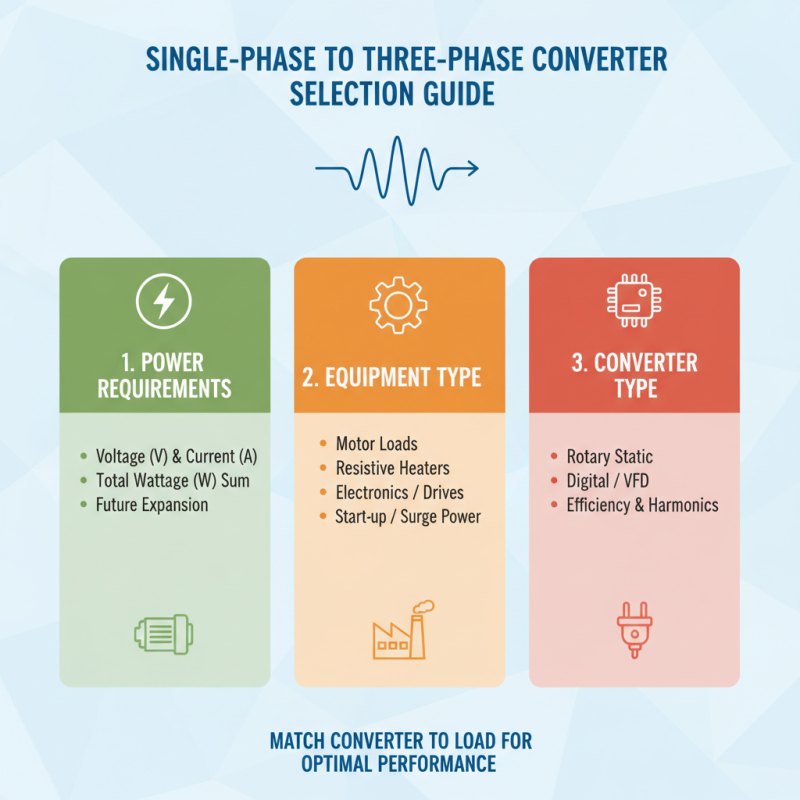
When selecting a single-phase to three-phase converter, it is crucial to identify the specific power requirements of your equipment. This involves understanding not only the voltage and current rating of the devices you intend to use but also their operational characteristics. Consideration must be given to the total power consumption, which typically involves summing the wattage of all devices that will be connected to the converter. This ensures that the converter can handle the total load without overheating or failing.
Additionally, the type of equipment plays a significant role in the selection process. Induction motors, for instance, often require a brief surge of power during startup, known as inrush current, which can be significantly higher than their running current. Therefore, it is essential to account for these peak demands when evaluating potential converters. Knowing the specifics of the operational environment, such as the frequency of use and durability needs, will further aid in determining the most appropriate converter type and size to meet your operational demands effectively.
Evaluating Different Types of Single Phase to Three Phase Converters
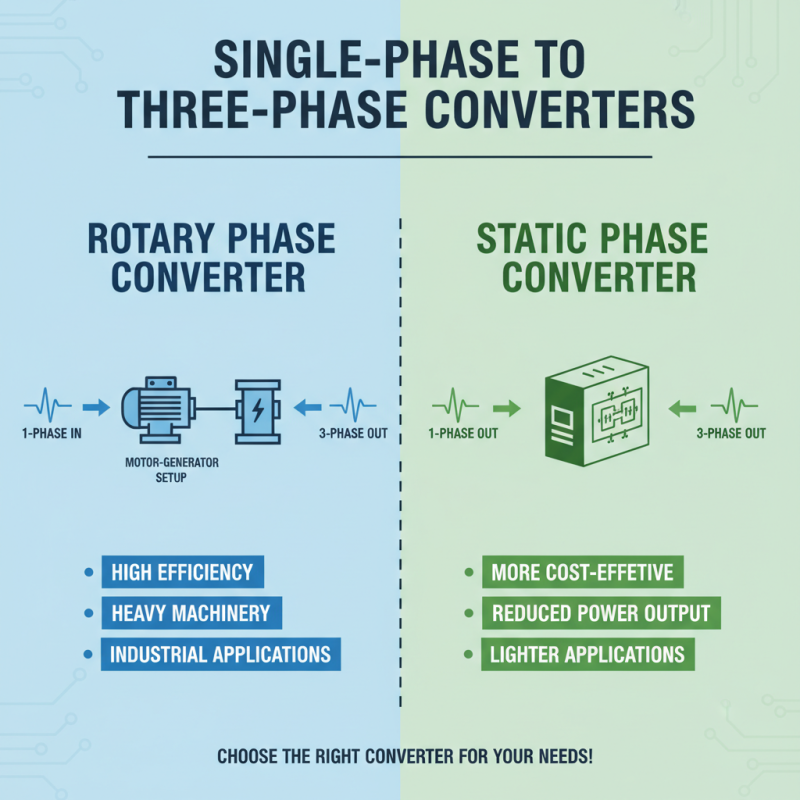
When evaluating different types of single phase to three phase converters, it's essential to consider the specific requirements of your applications. One common type is the rotary phase converter, which utilizes a motor-generator setup to convert single-phase power to three-phase. This method is highly efficient and suited for running heavy machinery. On the other hand, static phase converters are more cost-effective and straightforward but can result in reduced power output, making them ideal for lighter applications.
Tips: When selecting a converter, assess the total horsepower needed for your equipment. Ensure that the converter can handle the start-up load, especially for compressors or larger machinery. Additionally, think about the frequency of use—if you plan to run the equipment continuously, a rotary converter may offer better long-term benefits.
Another type to consider is the digital inverter-based converter. These converters allow for more precise control of the output and are generally lighter and quieter than rotary converters. They are perfect for applications that require speed control or variable torque. However, it's critical to evaluate the power quality needed for your specific applications to ensure compatibility.
Tips: Always check the voltage and current ratings of both the converter and your machinery. If possible, consult with a professional to determine which type best meets your particular operational needs and environment. Understanding the operational characteristics of each type will guide you toward making the best choice for your three-phase power conversion needs.
Key Features to Consider in a Converter for Optimal Performance
When choosing a single-phase to three-phase converter, several key features will significantly influence its performance and suitability for your specific applications. First and foremost, consider the converter's power capacity. This is measured in horsepower or kilowatts and needs to match or exceed the total load of the equipment it will be powering. An undersized converter may lead to motor overheating or failure, while an oversized unit could result in inefficiencies and increased operating costs. It's essential to have accurate power requirements for all machinery connected to the system.
Another critical aspect is the type of conversion technology employed by the converter. There are various technologies available, including rotary, static, and digital converters, each offering different advantages depending on the application. Rotary converters are generally more robust and can handle fluctuating loads more efficiently, while static converters may be more compact and can be an economical choice for stable, predictable loads. Furthermore, consider additional features like starting torque capability and harmonics management, which can influence the overall system performance and longevity. Understanding these features will help ensure that the converter you choose aligns well with your operational needs and provides reliable service over time.
Installation and Maintenance Tips for Your Chosen Converter
When selecting a single phase to three phase converter, installation and maintenance play crucial roles in ensuring optimal performance and longevity. According to a report by the International Society of Automation (ISA), improper installation can lead to a 20% increase in energy consumption, significantly affecting operational efficiency. To avoid this, it is vital to follow the manufacturer's guidelines closely and engage qualified professionals for installation. Proper groundwork, including assessing the voltage requirements and load demands, lays the foundation for seamless operation. Additionally, integrating preventative measures such as circuit protection devices can help mitigate risks associated with power surges.
Once the converter is installed, maintenance becomes paramount. Regular inspections, at least biannually, are recommended to identify potential issues such as overheating or wear and tear on components. The National Electrical Contractors Association (NECA) indicates that routine maintenance can extend the life of converters by up to 30%. Keeping the converter clean and free from debris, as well as ensuring proper lubrication of moving parts, can prevent performance deterioration. Additionally, staying updated with software or firmware updates can enhance functionality and efficiency, ensuring the system operates at peak performance. By prioritizing installation and maintenance, users can maximize their investment in a phase converter while ensuring reliability in their operations.
Related Posts
-

How to Seamlessly Upgrade from Single Phase to Three Phase Power Systems
-

Understanding the Mechanisms Behind Single Phase to Three Phase Converters in Modern Energy Systems
-

Top Single to Three Phase Converter Solutions for 2025 You Need to Know
-

Unlock Equipment Efficiency: How a 60Hz to 50Hz Frequency Converter Enhances Power Usage by 30%
-

Exploring the Impact of Rotary Phase Converters on Industrial Growth at the 2025 China 138th Import and Export Fair
-

Understanding the Benefits of Phase Converters: Transforming 1-Phase to 3-Phase Power Efficiently