How to Choose the Right VFD Controller for Your Application?
Choosing the right VFD controller can be a daunting task. Each application requires specific features and capabilities. As industry expert John Smith states, "A well-selected VFD controller can enhance efficiency and prolong equipment life." This insight highlights the significance of making informed choices.
Understanding the unique requirements of your application is crucial. Factors such as load type, control method, and environment can influence your decision. For example, a pump system may have different needs compared to a conveyor. The right VFD controller optimizes performance, but choosing poorly can lead to inefficiencies.
Visualizing the control interface, communication options, and installation complexity can provide clarity. A controller that seems perfect on paper may fall short in real-world applications. It's essential to reflect on past experiences and learn from them. Each choice is a step toward better understanding what truly works in your situation.
Understanding the Basics of VFD Controllers and Their Applications
Variable Frequency Drive (VFD) controllers are essential for motor control. They manage the speed and torque of electric motors. Understanding how they work is crucial for selecting the right one.
VFDs adjust the frequency of electric power. This modulation directly affects motor performance. Different applications may demand varying levels of control. For example, a pump might require precise speed regulation. In contrast, a conveyor might prioritize quick starts and stops. Knowing the specific needs of your application guides your choice.
However, not all VFDs are alike. Some may not work well in high-humidity environments. Others could struggle in extreme temperature conditions. It's important to assess the environment. Consider operational factors, too. Will the VFD be used continuously or intermittently? Each detail shapes the final decision. Your choices matter, and small oversights can lead to inefficiencies.
How to Choose the Right VFD Controller for Your Application?
| Parameter | Description | Typical Range | Application Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Voltage Rating | The maximum voltage the VFD can handle. | 100V - 600V | Pumps, Fans, Conveyors |
| Power Rating | The output power capacity of the VFD. | 0.5 kW - 500 kW | Industrial motors, Elevators |
| Control Method | The method used for controlling motor speed. | V/f control, Vector control | Textile machines, Cranes |
| Interface Type | Type of user interface provided. | Digital, Analog, Remote | HVAC systems, Water treatment |
| Protection Features | Built-in protections against faults. | Overload, Short circuit, Under-voltage | Manufacturing, Mining equipment |
Identifying Key Factors to Consider When Choosing a VFD Controller
Choosing the right Variable Frequency Drive (VFD) controller can be challenging. Several factors influence the decision-making process. Start by evaluating your specific application. Consider the type of motor, its power requirements, and the operating environment. In some cases, a simple controller might suffice. In others, you may need advanced features.
Look at the control method you plan to implement. Speed control may vary greatly based on what you need. For instance, closed-loop control offers precision for complex tasks. Additionally, analyze the energy efficiency of the options available. Sometimes, cost-effective solutions can lead to higher energy bills in the long run.
Don't ignore compatibility with existing systems. Sometimes, a controller may not interface well with older equipment. This could lead to increased downtime during installation. Installation challenges can also arise due to varying technical requirements or training needs. It’s important to weigh these considerations carefully. Each factor plays a role in ensuring optimal performance and long-term satisfaction with your choice.
Evaluating the Compatibility of VFD with Your Equipment
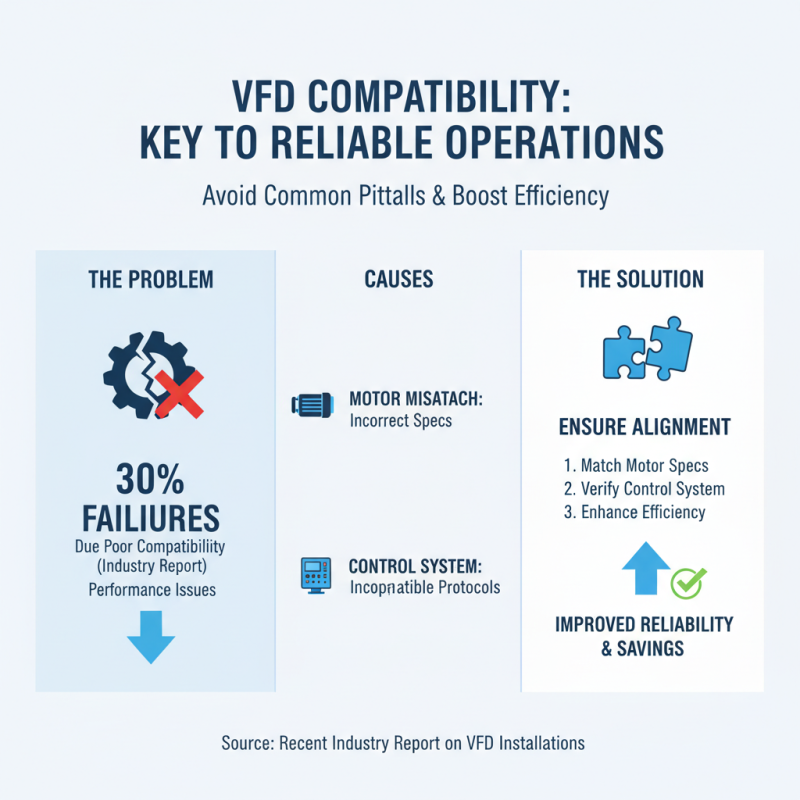
When selecting a Variable Frequency Drive (VFD), compatibility with existing equipment is crucial. A recent industry report indicates that over 30% of VFD installations fail due to poor compatibility. Performance issues can arise when a VFD does not match the specifications of the motor or the control system. Ensuring alignment can significantly enhance operational efficiency.
It's vital to consider the motor type. For instance, induction motors typically require different settings compared to synchronous motors. The power ratings should also correspond correctly. A VFD that's too powerful may lead to inefficiencies. Conversely, an underpowered VFD can cause damaging overload. Moreover, inspecting the communication protocols is essential. If the VFD cannot communicate seamlessly with sensors or control panels, it’ll hinder overall functionality.
Installation considerations are often overlooked. Poor integration can create performance bottlenecks. For example, a lack of proper shielding can induce noise, affecting signal quality. Users should also evaluate environmental factors. Dust and humidity can impact VFD performance, particularly in industrial settings. A mismatch in environmental tolerance can lead to premature failure or suboptimal operating conditions.
Assessing Environmental and Operational Conditions for VFD Selection
When assessing environmental and operational conditions for selecting a Variable Frequency Drive (VFD) controller, several factors must be considered. The operating temperature is crucial. If the environment is too hot or too cold, the VFD may not function optimally. Dust and moisture levels also play a role. A dusty or humid environment can lead to malfunctions, so adequate protection is necessary.
Consider the type of motor and load as well. Different applications require different torque and speed control. For instance, a pump may need a different VFD than a conveyor system. Analyze the load characteristics closely; constant or variable loads will influence the VFD choice. Sometimes, the necessary specifications might not be clear at first.
Electrical supply conditions cannot be overlooked. Voltage fluctuations or harmonics may affect performance. A well-designed system should anticipate these issues. Users may not always monitor conditions closely. This can lead to mismatched components and inefficiencies. The goal must always be to ensure compatibility, keeping in mind both the immediate and future operational environment.
Comparing Different VFD Technologies and Features for Your Needs
When choosing a Variable Frequency Drive (VFD) controller, it's essential to consider various technologies and features. One common technology is the Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) method. This method offers high efficiency and better speed control. However, it may introduce electrical noise, which can affect sensitive equipment. Understanding these nuances is vital for optimal performance.
Another technology is the Direct Torque Control (DTC). It provides superior torque management. This feature is beneficial when precise motor control is required. Yet, DTC can be more complex to implement. It's important to weigh this against your application needs. Less experienced users might overlook these complexities, leading to operational challenges.
Additionally, the control method affects the application. VFDs can be sensorless or use feedback devices. Sensorless drives are simpler and often more cost-effective. However, they may not perform well in all scenarios. Evaluating your specific application is key. This ensures the drive you choose aligns with both your performance and budgetary requirements.
Related Posts
-
How to Choose the Right VFD Controller for Your Industrial Applications
-

Top 10 Frequency Inverter Benefits You Must Know in 2023
-

Why Use a Frequency Changer for Your Electrical Needs?
-

Exploring Unique Alternatives to Rotary Frequency Converters for Enhanced Efficiency
-

Comprehensive Guide to Choosing the Right Voltage Frequency Converter for Optimal Performance
-

How to Choose the Right Solid State Phase Converter for Your Business Needs