How to Convert 60Hz to 50Hz Safely and Effectively?
In today's globalized world, converting 60Hz to 50Hz is an important topic. Many devices are designed for specific frequency standards, affecting their performance in different regions. According to a recent report by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), about 50% of electrical appliances used in Europe were originally made for a 50Hz supply. This highlights the necessity for a seamless transition between different frequency systems.
Dr. Robert Lang, an electrical engineer and frequency conversion expert, once stated, “Adapting equipment to different frequencies is crucial for compatibility.” His insights underline the complexities involved in converting 60Hz to 50Hz. This process is often fraught with challenges, including potential damage to appliances if not done correctly.
Successful conversion relies on the right tools and methods, as improper techniques can lead to inefficiencies. Specific considerations, such as voltage levels and frequency stability, must also be taken into account. Without proper knowledge, users may face unexpected issues after conversion. Understanding the risks and employing effective strategies is essential for safe operations in this area.

Understanding the Difference Between 60Hz and 50Hz Electrical Systems
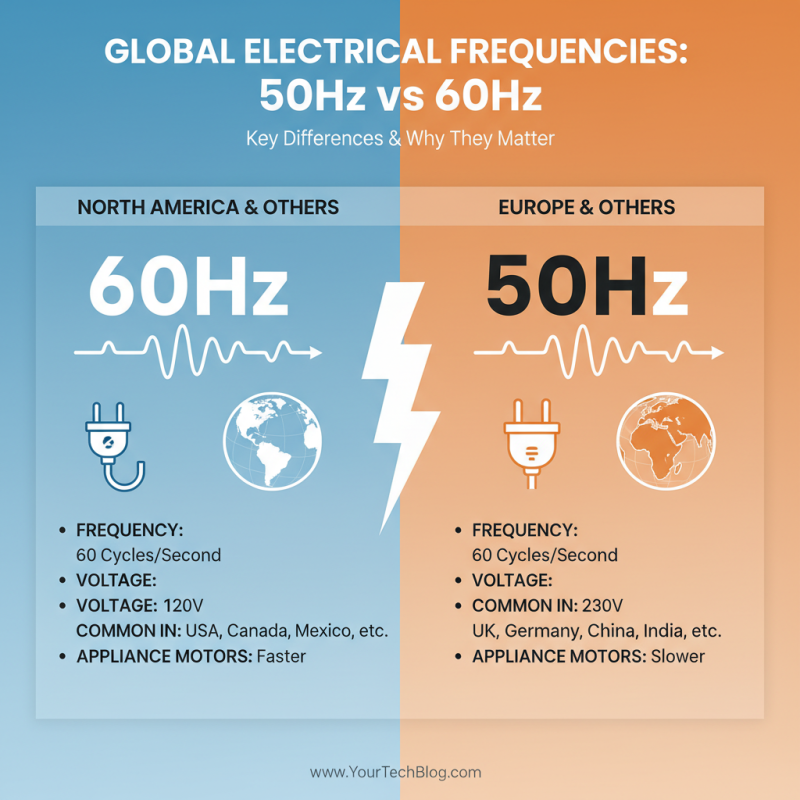
Electrical systems worldwide use different frequencies. The two main systems are 60Hz and 50Hz. These numbers reflect how many cycles per second the current oscillates. In North America, most devices run at 60Hz. In contrast, Europe and many other regions prefer 50Hz. Understanding this difference is crucial when converting systems.
Using a device designed for 50Hz in a 60Hz system can lead to issues. For example, motors may run faster, which can cause overheating. It’s essential to check if your equipment can handle this difference. Some devices may need an external converter. This converter can assist in managing the frequency correctly. However, not all converters work the same way; some may be ineffective or even unsafe.
Moreover, adjusting your appliances is more than a simple plug-in. Some devices may not operate correctly at the different frequency. It can damage electronics over time. Therefore, understanding how your specific device functions is paramount. Always consult information specific to your needs. Not all equipment is created equal. Be cautious as you explore these transitions.
Identifying Devices That Require Frequency Conversion
When converting 60Hz to 50Hz, it's crucial to recognize which devices need this frequency adjustment. Many household appliances, like refrigerators and microwaves, typically run on 60Hz. However, some machinery or electronics designed for the European market might only operate on 50Hz. This mismatch can lead to operational failures. It's essential to check each device's specifications before attempting any conversion.
Tips for identifying devices that require frequency conversion: Look for a label specifying the input frequency. This label is often found on the back or underside of the device. If the appliance is rated for 50Hz, you should consider using a frequency converter. Not all devices will function correctly on an incorrect power supply. The risks include overheating, buzzing noises, and even damage.
Try to keep your environment organized when doing these checks. Gather all devices in one spot. This makes inspections easier and reduces the chance of overlooking anything important. Reflect on the potential effects of using devices without proper frequency. It can save you from costly repairs or replacements in the long run.
Methods for Converting 60Hz to 50Hz Safely
When converting 60Hz to 50Hz, several methods can ensure a safe and effective transition. One common approach is using a frequency converter. These devices can adjust the output frequency for your appliances. They come in various sizes and capacities, so it's crucial to choose one that matches your needs. Many do not consider the power rating. This can lead to equipment malfunction.
Another method involves replacing the motor in your devices. If you have essential machinery, consider this option. Rewiring for 50Hz can optimize performance. However, this process is complex. You should consult a professional with experience in this area. The risk of injury or damage is real if done incorrectly.
Be mindful of the power supply. A constant voltage is vital in this process. Inconsistent voltage can damage sensitive electronics. It's also important to reflect on the cost of the conversion. Sometimes, it might be more economical to replace equipment. The choice between conversion and replacement is not always straightforward. Each scenario requires careful consideration and planning.
60Hz to 50Hz Conversion Methods Overview
Using a Frequency Converter: Installation and Operation
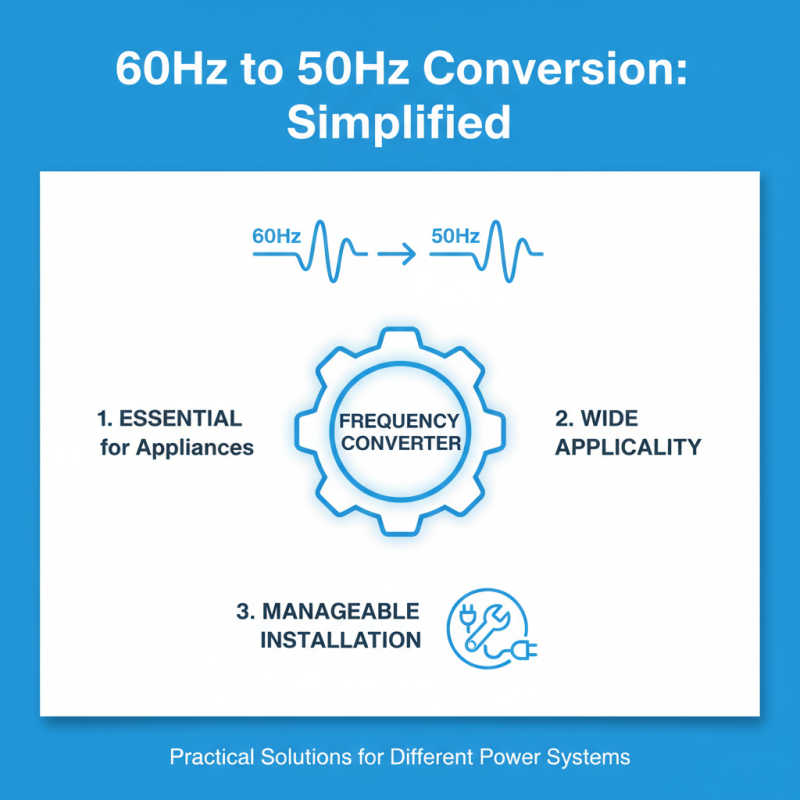
When converting 60Hz to 50Hz, using a frequency converter is essential. It's a practical solution for many appliances designed for different power systems. Installation might seem daunting, but with proper guidance, it becomes manageable.
Before installation, make sure to choose a suitable location for the converter. It should be dry and well-ventilated. Avoid crowded areas. Ensure it's not exposed to direct sunlight. It's unwise to rush through the setup. Planning your space ahead can save you a lot of trouble later.
Tips: Regularly check the wiring. Faulty connections can lead to inefficiencies. Also, read the user manual thoroughly. Understanding the converter's settings is crucial for optimal operation. Small mistakes here can cause significant problems later.
After installation, you may need to adjust settings based on your appliance’s requirements. Test the converter with less critical devices first. This helps ensure everything works smoothly. Some users overlook troubleshooting methods when issues arise. Staying informed about these can save you from unnecessary stress.
Best Practices for Ensuring Electrical Safety During the Conversion
Converting 60Hz to 50Hz can be challenging. Safety during this process is critical. Experts recommend using a frequency converter. A reliable converter can ensure proper voltage and current levels. According to a report by the International Electrotechnical Commission, improper conversions can lead to equipment damage.
Ensure that professionals handle the installation. It can be risky to attempt this on your own. Regular checks on the converter are essential. Observing temperature fluctuations and sound changes can prevent major failures. Too often, operators overlook these signs. Simple maintenance could avert costly repairs down the line.
Understanding load characteristics is also important. The electrical load must match the converter's specifications. Mismatched loads can create safety hazards. Some users underreport energy demands. This often leads to equipment stress and possible risks. Document everything during the conversion. Clear records help monitor for any inconsistencies. Frequent assessments guarantee a safer environment for all.
How to Convert 60Hz to 50Hz Safely and Effectively? - Best Practices for Ensuring Electrical Safety During the Conversion
| Aspect | Recommendation | Safety Measure | Tools Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| Conversion Method | Use a Frequency Converter | Ensure proper grounding | Frequency Converter |
| Installation | Hire a Licensed Electrician | Test installation before use | Multimeter, Safety Gear |
| Load Compatibility | Check Equipment Ratings | Use appropriate adapters | Voltage Meter |
| Testing | Perform Load Tests | Monitor for overheating | Thermal Camera, Load Tester |
| Maintenance | Regular Inspections | Keep documentation | Inspection Tools |
Related Posts
-

How to Convert 60Hz to 50Hz Easily at Home without Any Complications
-

5 Essential Facts About 50hz to 60hz Frequency Converters You Should Know
-

The Future of Energy Solutions Understanding the Importance of Hz Converter Technology
-
What is a Frequency Changer and How Does It Work in Modern Applications
-

2025 Guide: How to Use a 60 Hz to 50 Hz Frequency Converter Effectively
-

Why Use a Frequency Changer for Your Electrical Needs?