What is a Frequency Changer and How Does It Work in Modern Applications
In the realm of electrical engineering and power systems, a frequency changer plays a pivotal role in aligning the operational requirements of various devices and grids. As alternating current (AC) systems operate at specific frequencies, the need for frequency conversion arises when different systems require disparate frequencies for optimal functionality. This device, often referred to as a frequency changer, facilitates the conversion of power from one frequency to another, thereby enabling compatibility between varied electrical systems and enhancing the overall efficiency of power distribution.
Modern applications of frequency changers are vast and varied, spanning industries such as telecommunications, renewable energy, and manufacturing. By harnessing the capabilities of frequency changers, engineers can optimize equipment performance, improve energy efficiency, and accommodate the integration of renewable energy sources like wind and solar power, which may produce electricity at different frequencies. The versatility of frequency changers also lends itself to various technological innovations, making them essential for advancing smart grid technologies and ensuring that high-power systems operate seamlessly across different operational frequencies. As the demand for efficient power conversion continues to rise, understanding the functionality and applications of frequency changers becomes increasingly important in modern electrical engineering.

Definition of Frequency Changer and Its Mechanism

A frequency changer, also known as a frequency converter, is an electrical device that alters the frequency of an input signal to a different output frequency. This mechanism is vital in various applications, ranging from industrial motors to renewable energy systems. The general process involves the conversion of AC (alternating current) frequencies, where the device captures input energy, modifies its frequency through a series of electronic components, and outputs it at the desired frequency. This capability is crucial in adjusting the speed and torque of electric motors, enabling efficient operation in applications that require specific frequency ranges.
In modern applications, frequency changers are increasingly used in energy generation, particularly in wind turbines and photovoltaic systems. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global frequency converter market is projected to grow significantly, reaching USD 4.79 billion by 2025, driven by advancements in technology and the rising demand for energy-efficient solutions. Furthermore, frequency changers play a pivotal role in improving the performance and longevity of electrical equipment, as they allow for better control over operational parameters, reducing wear and tear on machines.
The working mechanism of frequency changers typically involves rectification, inversion, and filtering processes. Initially, the AC signal is rectified into DC (direct current) before it gets inverted back into AC at a different frequency. This process is accomplished using power electronics, particularly insulated gate bipolar transistors (IGBTs) and diodes. The efficiency of these devices has significantly improved over recent years; a recent study found that modern frequency converters can achieve efficiency levels of up to 98%, underscoring their importance in minimizing energy loss and enhancing system performance in various industrial applications.
Types of Frequency Changers Used in Modern Applications
Frequency changers are essential devices widely used in various industries to convert electrical energy from one frequency to another. In modern applications, several types of frequency changers are employed, each tailored to specific needs and operational scenarios.
One common type is the static frequency changer, which utilizes thyristors and converters to achieve frequency conversion without moving parts, resulting in higher efficiency and reliability. According to a report from the International Electrotechnical Commission, static frequency changers have seen a rise in adoption across renewable energy sectors, particularly in wind and solar farms, where they help in optimizing power output by adjusting the frequency to match grid requirements. Moreover, these devices are increasingly used in traction systems for trains and subways, contributing to smoother operation and energy savings.
Another prevalent type is the rotary frequency changer, which includes mechanical components such as synchronous motors and generators. These changers are particularly valued in industrial settings that require high power and robust performance. A study from the IEEE Power Electronics Society highlights that rotary frequency changers are preferred in applications involving large rotary equipment, such as pumps and compressors, where maintaining constant power quality is critical. Their capacity to handle varying loads while offering stable frequency output makes them indispensable in sectors such as manufacturing and oil and gas.
Industrial Applications of Frequency Changers in Power Systems
Frequency changers play a crucial role in modern industrial applications, particularly within power systems. These devices are essential for converting the frequency of electrical power, allowing for greater flexibility in the operation of industrial machinery. In industries such as manufacturing, the need for equipment that operates efficiently at different frequencies is vital, especially when integrating machinery from various regions where the standard power supply frequency may differ. By using frequency changers, industries can optimize equipment performance, reduce energy consumption, and minimize operational costs.
In power generation and distribution, frequency changers facilitate the interconnection of renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar power, with traditional power grids. These renewable sources often produce electricity at variable frequencies, and frequency changers help stabilize and synchronize this power output with the grid’s frequency standards. This capability not only enables the integration of green technologies but also enhances the reliability and efficiency of the power supply. Furthermore, frequency changers are employed in automation systems and drives, where they allow for precise control of motor speeds and torque, thereby improving the overall productivity of industrial processes.
Role of Frequency Changers in Renewable Energy Integration
Frequency changers play a pivotal role in the integration of renewable energy systems into the existing power grids. As renewable energy sources such as wind and solar become more prevalent, the variability of their output necessitates advanced technologies to ensure compatibility with conventional generation and distribution systems. According to the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), the global share of renewable energy in total power generation reached approximately 29% in 2020, driving demand for systems that can manage this fluctuating power efficiently.
Frequency changers, by converting alternating current (AC) power from renewable sources to different frequency levels, facilitate better synchronization with the grid and enhance the reliability of energy supply. In modern applications, frequency changers are essential for optimizing the performance of renewable energy systems. These devices allow for the adjustment of voltage and frequency to match grid requirements, enabling smoother energy distribution and reducing losses during transmission.
The U.S. Department of Energy reported that utilizing frequency changers in conjunction with energy storage systems can improve grid resilience and efficiency by up to 15%. Additionally, they assist in frequency regulation, which is crucial for maintaining the stability of electrical networks amidst the increasing share of intermittent renewable sources. Overall, the advancement of frequency changers is key to leveraging renewables effectively and achieving a cleaner energy future.
Future Trends and Innovations in Frequency Changer Technology
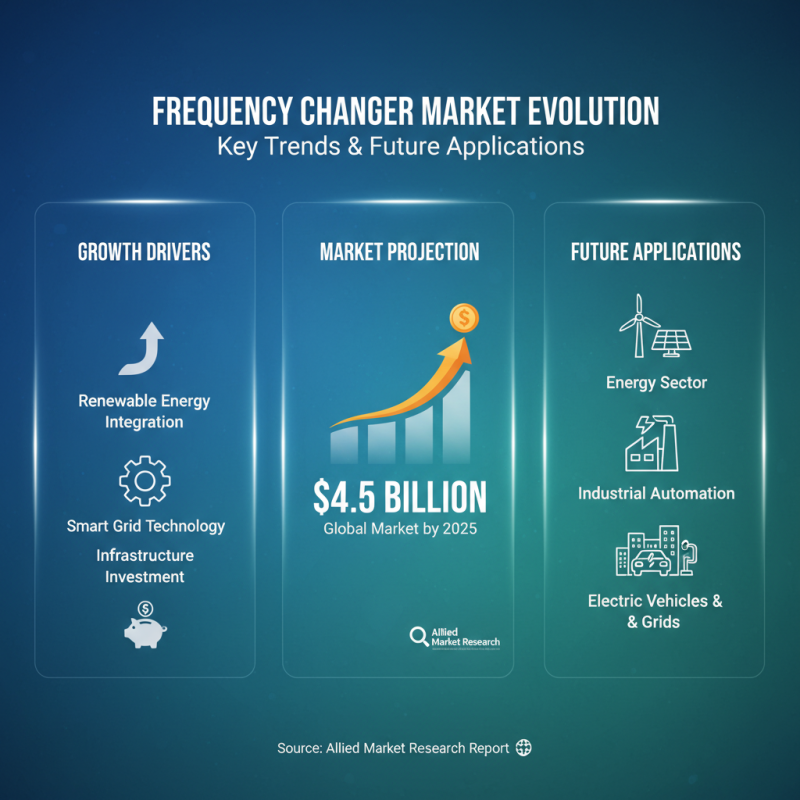
The technology behind frequency changers is evolving rapidly, with significant trends shaping their future applications in various industries. As the demand for renewable energy sources grows, frequency changers play a crucial role in integrating these systems into existing power grids. According to a recent market research report by Allied Market Research, the global frequency changer market is projected to reach approximately $4.5 billion by 2025, driven primarily by advancements in smart grid technology and increased investments in infrastructure.
Innovative designs, such as modular frequency changers, are gaining traction due to their enhanced efficiency and flexibility. These modular designs allow for easy scalability, making them suitable for both small-scale and large-scale power applications. Additionally, the emergence of solid-state frequency changers, which offer increased reliability and lower maintenance costs compared to traditional mechanical systems, is expected to revolutionize the market. With the growing emphasis on energy efficiency and sustainability, the adoption of frequency changers equipped with advanced features such as real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance is anticipated to become standard in modern electrical systems, ensuring optimal performance and longevity.
Related Posts
-

Exploring Unique Alternatives to Rotary Frequency Converters for Enhanced Efficiency
-

How to Choose the Right Voltage Frequency Converter for Your Needs
-

Unlocking Efficiency: How 3 Phase Frequency Converters Revolutionize Industrial Operations
-

What Is a 3 Phase Frequency Converter and How Does It Work
-

The Future of Solid State Frequency Converters Redefining Power Management
-

Comprehensive Guide to Choosing the Right Voltage Frequency Converter for Optimal Performance