What is a Frequency to Voltage Converter and How Does it Work?
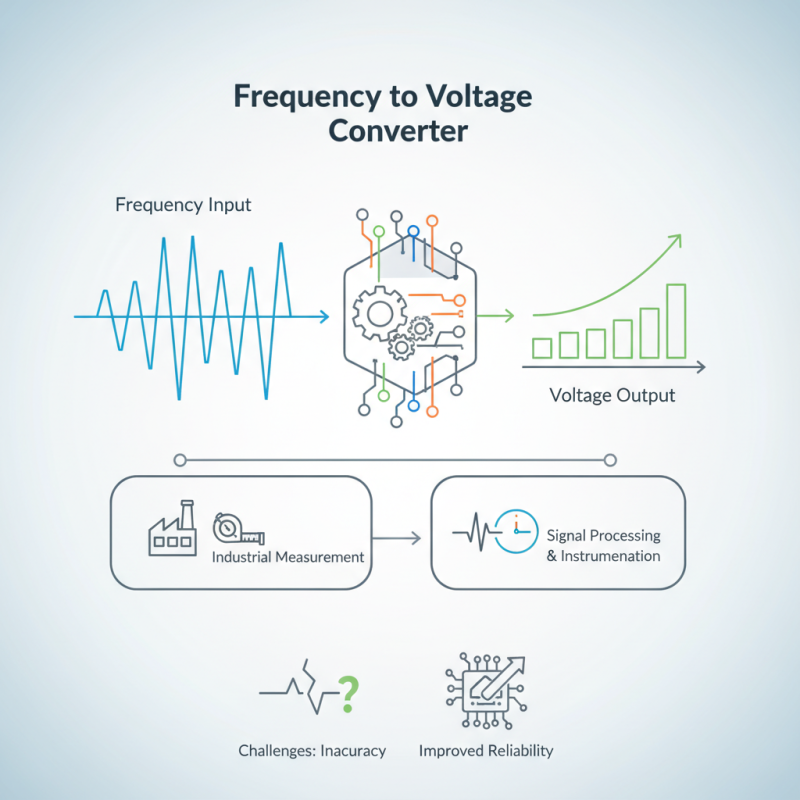
A frequency to voltage converter is an essential electronic device. It transforms frequency signals into corresponding voltage levels. This process finds significant applications in various fields. Industries often rely on these converters to ensure accurate measurements.
Understanding how a frequency to voltage converter works is crucial. The device captures input signals, typically frequency-modulated, and outputs a smooth voltage signal. This transformation is vital for converting data into a more manageable form. Common uses include signal processing and instrumentation.
While this technology is powerful, challenges exist. Variations in input frequency can lead to inaccurate voltage readings. Designers must address these imperfections. Knowing the limitations of frequency to voltage converters is important for optimal performance. Despite these issues, advancements continue to improve their reliability and accuracy.
Definition and Purpose of Frequency to Voltage Converters
Frequency to Voltage Converters (FVCs) are essential in many applications. They convert frequency signals into corresponding voltage levels. This conversion allows easier processing and interpretation of data. For instance, in automotive systems, FVCs help in monitoring engine parameters. They provide analog signals that reflect changes in engine performance.
The primary purpose of FVCs is to enable the use of frequency data in systems requiring voltage inputs. Many electronic devices rely on voltage signals to function. However, frequency signals are often more stable and easy to handle. FVCs bridge this gap, simplifying the integration of frequency-based sensors. However, achieving accuracy can be challenging. Noise can affect the output, leading to discrepancies.
In some cases, FVC designs may face limitations. For example, the conversion range can be narrow, restricting flexibility. Designers must consider these factors when developing or choosing an FVC. It's crucial to balance precision and complexity in these converters. Understanding specific application needs can help inform better design choices.
Frequency to Voltage Converter Output
This chart represents the output voltage corresponding to various input frequencies in a Frequency to Voltage Converter. The data shows how voltage varies with frequency, highlighting the relationship between the two parameters.
Basic Principles of Operation for Frequency to Voltage Converters
Frequency to voltage converters (FVCs) play a crucial role in electronic systems. They take an input frequency and convert it into a corresponding output voltage. This process is vital for many applications, including automation and data acquisition. Typically, these converters can be found in devices that measure rotation speed or in frequency modulation systems. According to industry reports, the global market for FVCs is expected to grow significantly, reaching valuations of over $5 billion by 2025.
The basic principles of operation for frequency to voltage converters revolve around the use of capacitors and resistors. The frequency signal is fed into the circuit, which integrates the frequency over time. This integration results in a voltage level that represents the frequency of the input signal. Various circuit designs can enhance the linearity and response time, ensuring accuracy in high-speed applications. For instance, a typical FVC's output can vary by 0.1% for certain frequency ranges, which can introduce errors in high-stakes situations.
While FVCs are reliable, challenges remain. Noise and temperature variations can affect performance. Engineers often need to spend considerable time calibrating their systems. Many designs still struggle to maintain low power consumption while achieving high accuracy. Addressing these issues requires ongoing innovation and careful measurement. As the demand for advanced frequency analysis grows, optimizing FVC performance will become even more critical.
What is a Frequency to Voltage Converter and How Does it Work? - Basic Principles of Operation for Frequency to Voltage Converters
| Parameter | Description | Typical Value |
|---|---|---|
| Input Frequency Range | The range of frequencies that the converter can accept as input. | 0.1 Hz to 100 kHz |
| Output Voltage Range | The range of voltages that can be produced as output. | 0 to 10 V |
| Linearity | The degree to which the output voltage is proportional to the input frequency. | ±1% full scale |
| Power Supply Voltage | The voltage required to power the device. | ±15 V or 5 V |
| Temperature Range | The operating temperature range that the converter can endure. | -40°C to +85°C |
| Response Time | The time it takes for the output voltage to stabilize after a frequency change. | < 1 ms |
Key Components of a Frequency to Voltage Converter System
Frequency to Voltage Converters (FVC) transform frequency signals into corresponding voltage levels. They are essential in various applications, including sensor technology and signal processing. The efficiency of these converters significantly relies on their key components.
The oscillator is a vital element. It generates a stable frequency signal. Precision in this component is crucial, as even minor inaccuracies can lead to skewed output. According to industry reports, an increase in oscillator precision can improve overall converter accuracy by over 30%. Filters are equally important. They remove unwanted noise, ensuring the signal remains clean. Poor filtering can result in unreliable voltage readings. Studies indicate that inadequate filtering can lead to errors exceeding 15% in output voltage.
Another key component is the analog-to-digital converter (ADC). It digitizes the voltage level for further processing. The speed and resolution of the ADC directly affect the system's overall performance. Reports show that higher resolution ADCs enhance system reliability by at least 25%. Balancing these components ensures a robust FVC design. However, challenges remain. Matching the components optimally is not always straightforward. Small variations in components can lead to significant changes in output. Addressing these details is crucial for effective performance.
Common Applications of Frequency to Voltage Converters
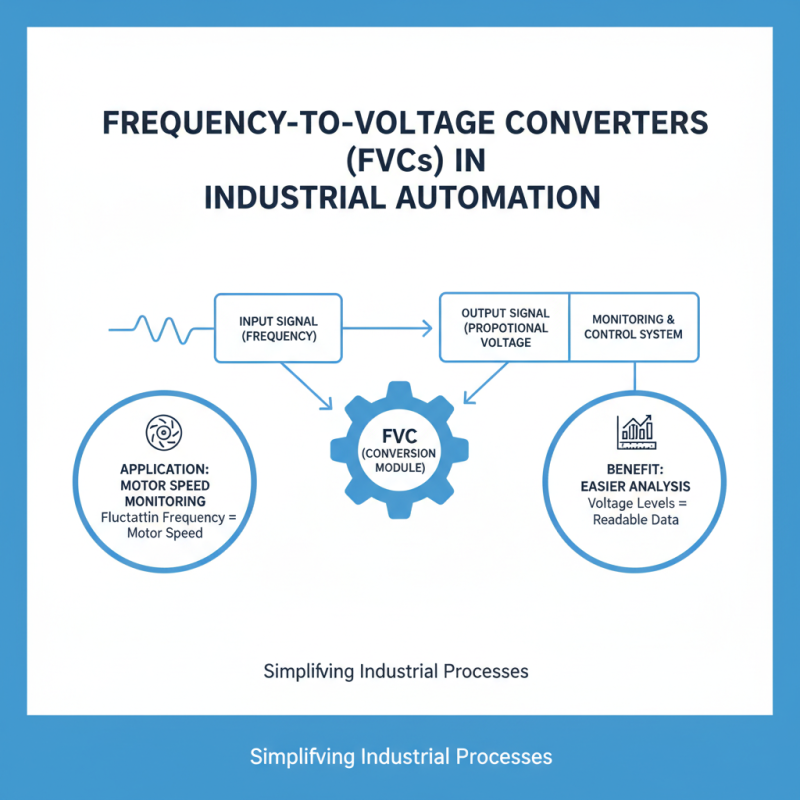
Frequency to voltage converters (FVCs) are widely used in various industries. One common application is in automation systems. In these systems, FVCs convert the frequency of an incoming signal into a proportional voltage. This conversion facilitates easier monitoring and control. For example, a fluctuating frequency can represent different speeds of a motor. The FVC translates these frequencies into readable voltage levels for more straightforward analysis.
Another significant use is in signal processing. Here, FVCs assist in analyzing frequency-modulated signals. Businesses often rely on these converters for measuring parameters like flow rates in industrial applications. By converting frequency to voltage, operators can assess flow levels efficiently. However, calibration challenges can arise, leading to inaccurate readings. Engineers must regularly check settings to avoid discrepancies.
In the field of telecommunications, FVCs help demodulate signals. They play a crucial role in ensuring clear communication. Cost-effective solutions using FVCs can enhance overall system performance. Despite their benefits, the complexity of integration with existing systems can pose difficulties. Users need to understand the limitations and challenges involved in the implementation process.
Advantages and Limitations of Using Frequency to Voltage Converters
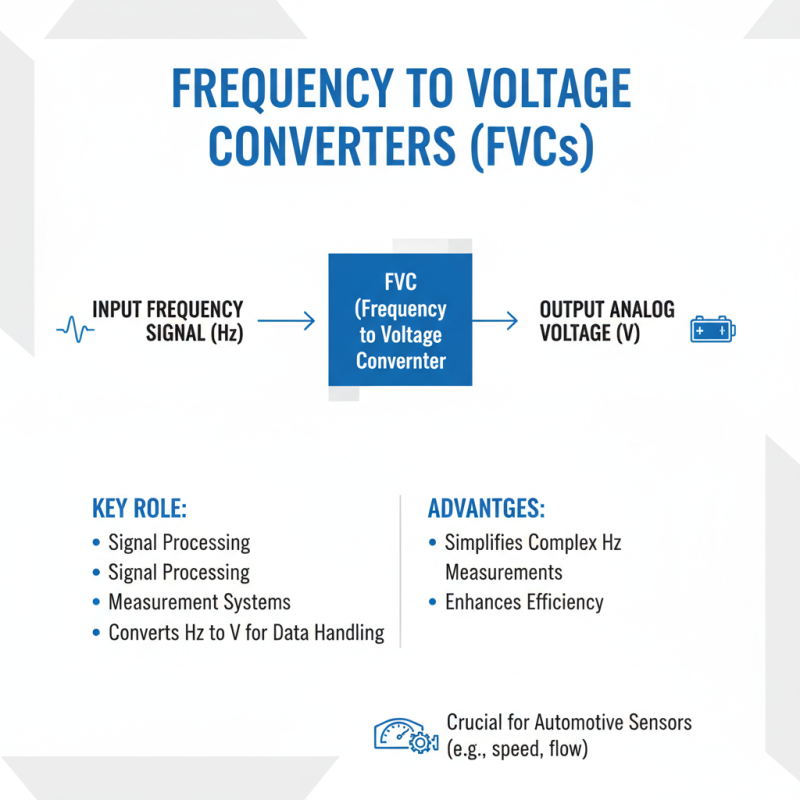
Frequency to voltage converters (FVCs) serve a critical role in various applications, especially in signal processing and measurement systems. These devices convert an input frequency into a corresponding voltage output, facilitating easier data handling. One advantage is their ability to simplify complex frequency measurements. This can significantly enhance efficiency in systems like automotive sensors, which often rely on accurate frequency translations.
However, FVCs are not without limitations. For instance, their accuracy can decline at higher frequencies. A study from a leading industry report indicates that over 20% of users reported inconsistencies in measurements beyond 10 kHz. Additionally, the linearity of output voltages may suffer in certain scenarios. Factors such as temperature fluctuations can cause drift in readings. This can be concerning, especially in precision applications. Each of these aspects calls for careful consideration when selecting a frequency to voltage converter for critical uses.
Related Posts
-
What is a Frequency to Voltage Converter and How Does it Work?
-

How to Effectively Utilize Frequency to Voltage Converters in Your Projects
-

Unlocking Market Trends for Frequency to Voltage Converters at the 138th Canton Fair 2025
-
2026 How to Choose the Right Voltage Converter for Your Needs?
-

Understanding the Essential Role of Power Converters in Modern Energy Systems
-

How to Choose the Right VFD Controller for Your Application?