2026 How to Choose the Right Voltage Converter for Your Needs?
Choosing the right voltage converter can be a daunting task. The market is flooded with options, each claiming to meet various needs. According to a recent report by the International Electrotechnical Commission, global demand for voltage converters is expected to grow by 12% annually.
Expert John Smith, a leading authority in voltage converter technology, states, "Understanding your power needs is crucial for selecting the right converter." This highlights the importance of assessing both voltage and power output. Many consumers overlook these factors, risking device damage or inefficiency.
Selecting an appropriate voltage converter involves evaluating devices' voltage requirements. It is necessary to consider wattage ratings and compatibility. Failing to do so can lead to inadequate power supply, resulting in performance issues. Awareness of this is vital for efficiency and safety. Ultimately, the right voltage converter enhances device functionality and longevity.
Understanding Voltage Converters: Types and Functions
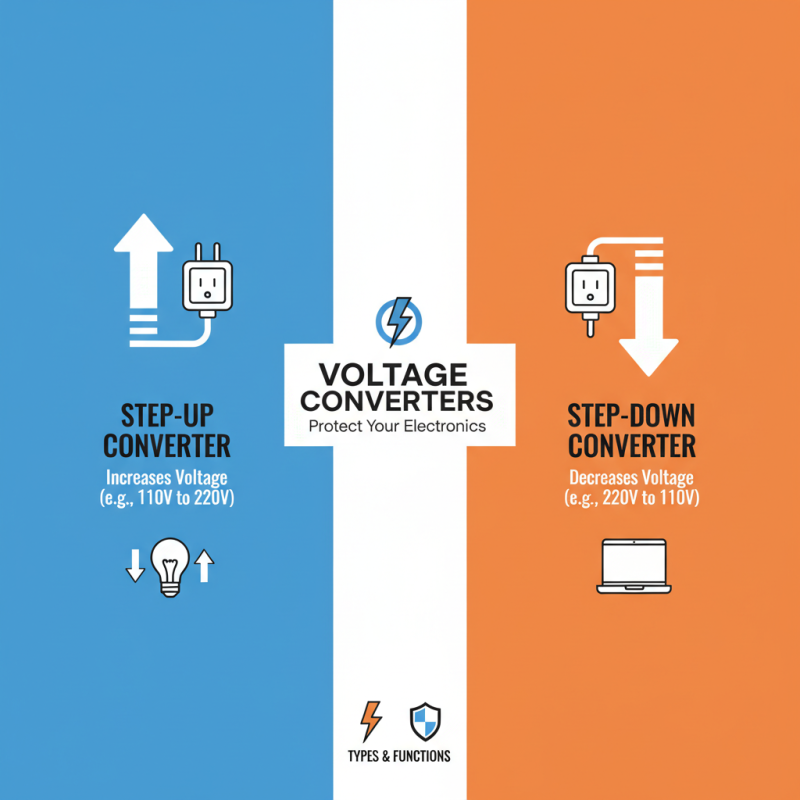
When choosing a voltage converter, understanding its types and functions is crucial. Voltage converters primarily fall into two categories: step-up and step-down. A step-up converter increases voltage, while a step-down converter decreases it. These devices ensure your electronics receive the appropriate voltage, preventing damage or poor performance.
Tips: Always check the voltage and wattage ratings of your devices. Mismatched ratings can lead to failure. It's essential to use a converter that matches your needs. If you're unsure about your requirements, consult the manuals of your devices.
Voltage converters have various features. Some include built-in safety mechanisms, such as overload protection. While handy, not all converters offer these features, leading to potential risks. Always choose wisely to avoid unpleasant surprises. Additionally, pay attention to the size and weight of converters. Compact models are more portable, but may not handle larger loads efficiently.
Assessing Your Power Requirements: Voltage and Wattage
When choosing a voltage converter, understanding your power needs is crucial. Start by assessing the voltage requirements of your devices. Different regions have varying voltage standards. For example, some use 110V while others rely on 220V. Knowing this helps avoid damage to your electronics.
Next, consider the wattage requirements. Each device has a power rating, usually found on the label. Calculate the total wattage of all devices you plan to connect. It’s essential not to exceed the converter’s wattage limit. Overloading can lead to overheating or failure.
Moreover, think about the type of devices you will use. Some equipment needs stable power, while others are more forgiving. It’s also important to consider the converter’s efficiency. High efficiency will save you energy in the long run. Ultimately, take time to evaluate your needs thoroughly. Sometimes, simpler solutions might actually serve you better.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Voltage Converter
When choosing a voltage converter, there are essential factors to consider. Power requirements are key. Assess the total wattage of your devices. Ensure the converter can handle more than what you need. Some users underestimate their needs and face issues later.
Next, consider the input and output voltage ratings. Different regions have varying standards. Make sure the converter matches the voltage of your devices. A mismatch can lead to damage or malfunction. Pay attention to plug types as well. Adapters may be necessary for compatibility.
Finally, think about portability. If you travel often, a lightweight, compact converter is ideal. However, these models may have lower power limits. Sometimes, convenience comes at a cost. Balancing size, weight, and functionality is crucial. Reflect on your priorities before making a choice.
Safety Standards and Certifications for Voltage Converters

When selecting a voltage converter, safety standards and certifications are crucial. Look for products that comply with international standards such as IEC and UL. These certifications ensure reliability and user protection. A report by the International Electrotechnical Commission states that certified devices significantly reduce risks of electrical fires and malfunctions.
Moreover, consider converters that carry CE marking. This indicates compliance with European health, safety, and environmental protection standards. According to a study by Electrical Safety Foundation International, products meeting these standards are 30% less likely to pose safety hazards. Always verify the presence of these certifications before making a purchase.
Be aware that not all voltage converters are created equal. Some may lack necessary certifications, leading to potential risks. Consumer safety must come first. Choose wisely and ensure that the converter meets your needs and safety requirements.
Practical Applications: When to Use Different Voltage Converters
When choosing a voltage converter, it's crucial to understand when to use different types. Many people use voltage converters during travel. For example, European devices may not work in North America due to voltage differences. A step-up converter is essential in this case. It changes a lower voltage to a higher one.
Consider your device's wattage before purchasing. Some converters cannot handle high wattage. If you try to use them for heavy equipment, they may burn out. This could lead to costly repairs or replacement. You need to evaluate the specific requirements of each device.
**Tips:** Always check the voltage output and input before using a converter. This is often overlooked. It's also wise to allow some buffer in wattage. For example, if your device consumes 50 watts, choose a converter rated for at least 75 watts. This helps prevent overheating.
Every situation is different. Sometimes, you may require multiple converters for various devices. This can complicate your travel plans. It’s best to simplify where possible. Ensure you are prepared with the correct converter to avoid inconvenience.
2026 How to Choose the Right Voltage Converter for Your Needs?
| Converter Type | Input Voltage (V) | Output Voltage (V) | Power Rating (W) | When to Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step-down (Buck) Converter | 90-240 | 5-30 | 100-300 | Powering low-voltage devices from higher voltage sources |
| Step-up (Boost) Converter | 1.5-12 | 12-60 | 50-200 | Increasing voltage for devices that require a higher input |
| Inverter | 12-48 | 110-240 | 300-2000 | Converting DC power to AC for household appliances |
| AC-DC Adapter | 100-240 | 5-24 | 30-150 | Powering devices directly from wall outlets |
| DC-DC Converter | 5-60 | 3.3-24 | 50-300 | Regulating voltage levels in electronic circuits |
Related Posts
-

Ultimate Guide to Selecting the Right Power Converter for Optimal Efficiency
-

Understanding the Essential Role of Power Converters in Modern Energy Systems
-

The Future of Energy Solutions Understanding the Importance of Hz Converter Technology
-

How to Choose the Best Single Phase to Three Phase Converter for Your Needs
-
Why You Should Choose a Rotary Converter for Your Power Needs
-

How to Convert 60Hz to 50Hz Easily at Home without Any Complications