Why Use a Frequency Changer for Your Electrical Needs?
In today's fast-paced electrical industry, the relevance of a frequency changer cannot be overstated. Experts like Dr. Alice Johnson, a leading engineer in power systems, assert, "The right frequency changer can optimize energy efficiency significantly." This statement highlights the crucial role of these devices in modern applications.
Frequency changers help in adjusting the frequency of power supply. They allow various machines to operate effectively at different frequencies. For instance, they enable equipment designed for a 60 Hz supply to run on a 50 Hz power line, ensuring seamless functionality.
However, not all applications yield the expected results. Some users face challenges, such as installation difficulties or inefficient performance. Understanding these nuances is essential for anyone investing in a frequency changer. Reflection on these points can guide choices, leading to better outcomes.

Introduction to Frequency Changers and Their Functionality
Frequency changers play a crucial role in various electrical applications. They adjust the frequency of electrical power to match the requirements of different systems. This is particularly important for industries using motors and generators. According to a report by Research and Markets, the global market for frequency changers is expected to reach $5 billion by 2025. This growth reflects the increasing demand for energy efficiency.
In practical terms, a frequency changer modifies the input frequency to ensure optimal performance. For instance, motors designed for 60 Hz may not operate efficiently at 50 Hz. An adjustment by a frequency changer allows these motors to function correctly. This technology enhances energy savings. However, implementation can be complex and requires careful planning. Some systems may face compatibility issues.
While frequency changers are beneficial, they are not without challenges. They can introduce harmonics, which may negatively impact nearby equipment. Additionally, choosing the wrong frequency changer could lead to inefficiencies. An analysis from the International Electrotechnical Commission suggests that proper selection is crucial for performance. Users must weigh the advantages against potential drawbacks. This requires a thorough understanding of the application and the system's needs.
Advantages of Using Frequency Changers in Electrical Systems
Frequency changers are essential in modern electrical systems. They adjust the frequency of electrical power to meet specific needs. This capability offers various advantages that enhance efficiency and performance.
One significant benefit is energy efficiency. A frequency changer allows motors to run at optimal speeds. This adjustment reduces energy waste. For example, in pumps or fans, operating at the right frequency can lower energy consumption. However, improper settings can lead to inefficiencies. Users must monitor system performance closely.
Another advantage is flexibility. Frequency changers enable compatibility with diverse equipment. Different machines may require unique frequency settings. Adapting to these requirements increases system versatility. Yet, the initial setup may be complex. Users should invest time in understanding the technical aspects to avoid potential pitfalls.
Embracing this technology can lead to enhanced system productivity and reliability in the long run.
Applications of Frequency Changers in Various Industries
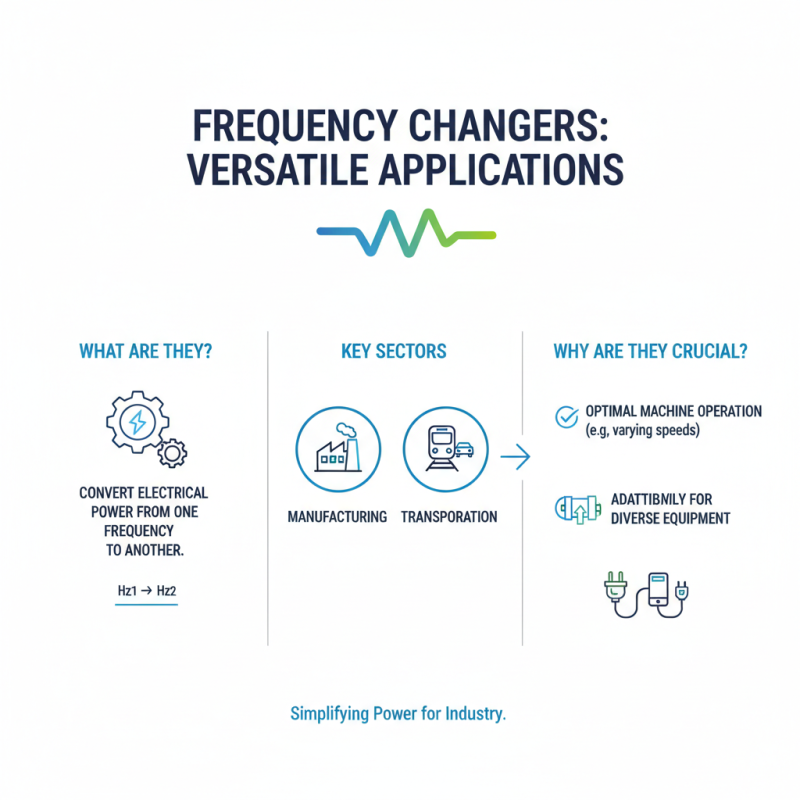
Frequency changers serve diverse applications across various industries. These devices convert electrical power from one frequency to another. This functionality is vital in sectors like manufacturing and transportation. For instance, in manufacturing plants, machines often require different frequencies to operate optimally. Equipment that runs on varying speeds can benefit greatly from this technology.
The renewable energy sector also utilizes frequency changers. Wind turbines and solar panels generate power at different frequencies. To align with the grid's requirements, frequency changers adjust the output. This process enhances energy efficiency and supports a stable power supply. However, integrating these systems can present some challenges. The complexity of installation and maintenance should not be overlooked.
Transport systems, particularly in rail, rely on frequency changers. Trains often operate on electricity that differs from standard grid frequency. Operating under optimal conditions enhances performance and reduces wear and tear. However, the initial cost and energy losses during conversion emerge as potential drawbacks. A careful assessment before implementation can lead to better outcomes.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Frequency Changer
Choosing the right frequency changer for your electrical needs requires careful consideration. Frequency changers convert power from one frequency to another. This is important for many applications, particularly in industrial settings. The type of machinery and equipment being powered will influence your choice.
When selecting a frequency changer, evaluate the load requirements. Different devices have varied power needs. A mismatch can lead to inefficiencies. In some cases, a frequency changer may be oversized or undersized for the application. Pay attention to output quality as well. An unreliable power output can damage sensitive equipment.
Additionally, consider the environmental conditions where the frequency changer will be used. Factors like temperature and humidity can affect its performance. Some devices are designed for harsh conditions; others are not. Be aware of maintenance needs too. Regular checks can prolong the lifespan of the equipment. Balancing these factors is key. Striking the right balance can lead to optimal performance and energy savings.
Frequency Changer Usage Across Different Industries
Maintenance and Troubleshooting Tips for Frequency Changers
Maintaining frequency changers is essential for optimal performance. Regular inspections help catch issues early. Many professionals overlook routine checks. This can lead to significant downtime. Data from industry sources indicate that 30% of maintenance issues arise from neglected equipment.
Monitoring key parameters is crucial. Voltage fluctuations can cause inefficiencies. Temperature readings should be consistent, too. If temperatures rise excessively, it may indicate underlying problems. Proactive maintenance can reduce repair costs by up to 40%, according to a recent study by the Electrical Engineering Association.
When troubleshooting, understand common fault symptoms. Unusual noises often signal mechanical wear. Sudden power losses can reveal electrical faults. Many technicians lack the experience to identify these issues quickly. Errors can escalate, resulting in expensive repairs. Frequent training is beneficial. It helps personnel recognize and resolve problems efficiently.
Related Posts
-
What is a Frequency Changer and How Does It Work in Modern Applications
-

Mastering the Basics: A Step-by-Step Guide to Using 3 Phase Frequency Converters
-

Exploring Unique Alternatives to Rotary Frequency Converters for Enhanced Efficiency
-

Comprehensive Guide to Choosing the Right Voltage Frequency Converter for Optimal Performance
-

How to Choose the Right Solid State Phase Converter for Your Business Needs
-

How to Choose the Right Voltage Frequency Converter for Your Needs